companies:krauss:krauss
Karl Louis Krauss - Krausswerke

| Established | 1887 | |
| Founder | Karl Louis Krauss (*April 25th, 1862; + December 5th, 1927) | |
| Adress(es) | Schwarzenberg/Saxony | |
| Operations | Sheet metal articles | |
| Production program | Jugs, funnels, oil cans, various containers, kerosene lamps and many more. Among other patented products, particularly famous are the „ “Triumph cradle swing“ (Picture from 1898 to the right > Source: A. Kohlschmidt: Sächsisches Obererzgebirge. Führer von Schwarzenberg und Umgebung. 2. Auflage. Schwarzenberg, Verlag von Max Helmert, 1898) and later the steam washing machines. |  |
| Brief history | 1887 - Established by Karl Louis Krauss, plumber and son of a spoon smith. 1891 - First expansion of factory space (staff about 50 employees) 1895 - Filing of patent (# 86351) for a hot-dip galvanized bathtub called “Krauss-Bathtub” which was later marketed as “Triumph cradle swing” (picture above). It was further developed and later produced in millions as the public bathtub with significant positive impact on public hygiene. 1906 - Installation of the first hot-dip galvanizing plant in the region. Treating iron/steel with a coat of 450 °C hot zinc is - once oxidized - a durable protection against corrosion for 50 years and beyond. Besides leading the factory, Karl Louis Krauss was actively participating in the local political and social life. He was curator of the „Fachschule für Blechbearbeitung“ in Aue to which I will dedicate a separate section “Schwarzenberg and Saxony as center of early sheet-metal fabrication in the pre WW I “German Reich”. Many more oil cans and related manufacturing companies originated in the “Erzgebirge”. The history of iron production and processing in the “Erzgebirge” goes centuries back and is worth a separate section as it was in the center of the industrial revolution in Germany. 1914-18 - World War I 1919 - Friedrich Emil Krauss (*March 29th, 1895), his second son (his brother died early in the war), is taking over the management while his father retired and moved to Dresden to focus solely on product design. At that time the company employed about 200 people. |
|
| 1920 - The „Krausschiffchen“, designed by Walter Kersting, was registered as trademark (see logo above). Prior to that a so-called “Rosehammer” was used (to the right: Souce Collection Lehmann) |  |
|
| With the change in management and logo, in two steps the company name was changed. On May 19th, 1919 from “Louis Krauss Metallwarenfabrik“ to „Krausswerke Louis Krauss“ and finally on January 12th, 1922 to „KRAUSSWERKE“. The letterheads in use for invoices are decorative examples of these changes (see letterheads from 1908, 1916 and 1940 to the right; Source:Digitalized collection of letterheads from the Industrial Museum of Saxony ) |  |
|
 |
||
 |
||
| 1927 - Karl Louis Krauss dies in a traffic accident 1935 - Krausswerke started participating in arms production (cable drums, food containers, car bonnets and other bod parts …) Till 1937 Friedrich Emil Krauss has filed more than 500 national and international patents ranging from washing machines to explosion-proof motorcycle tanks. His company by that time was the largest manufacturer of washing machines and bathtubs in Germany. In the same year Krausswerke was awarded for their social commitment to their workers and extraordinary economic achievements as „Nationalsozialistischer Musterbetrieb“ (Nazi regime model plant). 1938-45 - World War II during which civil production continued on a low level. Staff increase to 800 in 1939 and 1000 at the end of the war. |
||
| Post war summary: In the months directly after the end of the war F. E. Krauss was enjailed (till 1954) and his company expropriated and taken into trust administration*. By January 1946 all factory equipment was disassembled and transported to the East. In March of the same year government gave permission to restart production which was certainly a huge challenge given the circumstances.. On July 1st, 1947 the Krausswerke were renamed to VEB Erzgebirgische Waschgerätefabrik Schwarzenberg. About 70% of the factory was rented out and about 200 employees re-started the production. Initial products were equipment for harvesting and transporting potatoes and cattle muzzles. More details on the successor company can be found in the Wirtschafts-Chronik page 147 (details below). *For interested individuals I recommend a research paper issued 2015 by Leonore Lobeck. In this article the role of F.E. Krauss in Nazi Germany is laid out from a historic and the recent research perspective. He was NSDAP member and certainly benefitted from the regime. Recent research however leaves valid doubts whether characterizing him as ruthless promoter of Nazi-Germany and rude capitalist, as done after the war in the German Democratic Republic, is not a too single sided view on his lifetime contribution to the city, its inhabitants and the region. His fate is not an isolated case where formerly successful entrepreneurs and probably in modern terms “socially responsible good citizens” by engaging with the Nazi regime lost afterwards everything (whether justified or not is not on me to judge). For Friedrich Emil Krauss it meant losing control and ownership of his company and confiscation of his private possessions. In the age of 59 years he was released from prison and re-started from scratch to work in the Western part of Germany as industry consultant for Buderus in Wetzlar. He retired in 1973 with 76 years (!!) and died 1977 in Stuttgart. |
||
| Status 2021 | Expropriated 1945, disassembled and ultimately renamed mid 1947 to VEB Erzgebirgische Waschgerätefabrik Schwarzenberg. | |
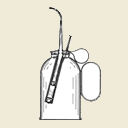
| Oil can history | Karl Louis Krauß initially started with manufacturing oil cans and other small sheet metal household items in his rapidly growing workshop. Around 1890 he employed already 8 employees. I have recently been able to acquire a catalogue from 1914 (just before WW I), the picture to the right shows some very nice oil cans. The very same picture is shown in the book that F.E. Krauss wrote about his father (page 33, details below). The manufacturing of oil cans, particularly after the major inventions in the early 20th century, producing oil cans was certainly not anymore a core business. Patents and adverts below however evidence that the company did still produce to some extent oil cans. | 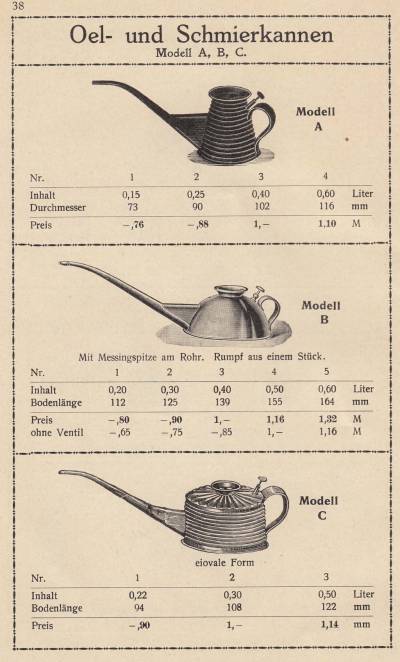 |
| Oil Cans | The bathtubs later produced used to carry the company logo & “KRAUSS”. Early oil cans (e.g. produced for the “Königlich Sächsische Staatseisenbahn (K.S.St.E)” used to have a soldered brass plate attached like the one to the right. Shapes shown are not unique and several other local companies produced them as well (e.g. Paul Hedrich in Schwarzenberg). |  |
| Oil can shown in the middle of the catalogue page above. |  |
|
| Patents | #DE_345557 granted to Friedrich Emil Krauss on December 13, 1921 | 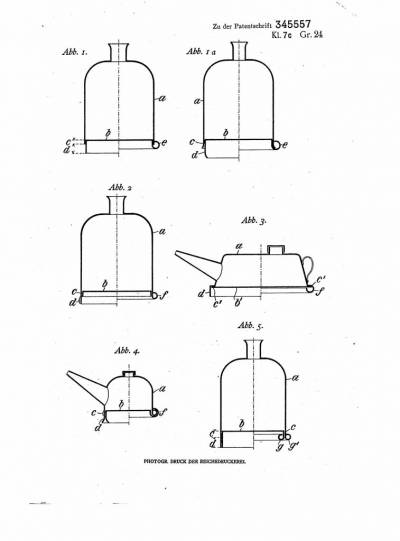 |
| Catalogue pages | The Pages of the 1914 catalogue will be published soon | |
| Adverts | Anyone able to date this pre-1920 advert more accurately? |  |
| Thanks to | Maximilian Lehmann for his wonderful website preserving the memory of Friedrich Emil Krauss | |
| Further references | Wikipedia articles on Karl Louis and Friedrich Emil Krauss Friedrich Emil Krauss: Das Leben meines Vaters Karl Louis Krauss; Schwarzenberg 1937 Fischer–Krauss, Käthe: Das Leben sei ein Lobpreis auf die Heimat. Mein Vater Friedrich Emil Krauss, Lahr 1998 Lobeck, Lenore: Friedrich Emil Krauß (1895–1977). Ein Unternehmer aus dem Erzgebirge. In: Zeitschrift des Forschungsverbundes SED-Staat 37/2015, S. 35-61. > Posted on the website mentioned above Wirtschaft-Chronik; Ein Streifzug durch die Wirtschaftsgeschichte der Stadt Schwarzenberg im Erzgebirge, herausgegeben von der Stadt Schwarzenberg anlässlich der 850-Jahr-Feier, 1. Auflage 2000 All of the named resources contain further references |
|
companies/krauss/krauss.txt · Last modified: by wikiadmin